In this article I will briefly summarize the traditional, converged and hyper-converged infrastructures.
Looking at the layers of x86 virtualization, the following basic components are seen;
- Physical server
- Virtualization software
- Storage
- Network devices
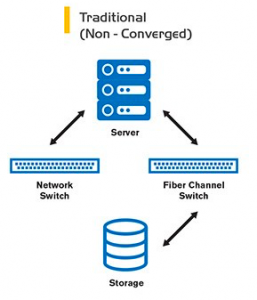
Traditional: When business continuity is not observed, local disks on the server can be used, if business continuity is required, access to storage units via the SAN or NAS protocols are Direct-Attached, San switch or Network switch can be called virtualization architecture. Related products can consist of different brands and may cause software or hardware compatibility issues or operational difficulties.
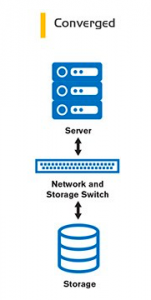
Converged: It is the infrastructure in which the hardware and software components in traditional architecture are transformed into a single package by the companies that create a manufacturer or business partnership. To reach the compatibility of the products used by the manufacturers, they have features such as single point support, easy update and quick setup. The product of VMware, Cisco and EMC jointly founded by VCE vBlock can be shown as an example.
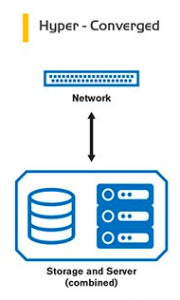
HyperConverged: Unlike traditional and converged architecture, only local disks on physical servers are used , removing the storage unit layer and passing it to the virtualization administrator of this management can ease the architecture. Products can be obtained from the a vendor as well as approved and compatible manufacturers can be supplied. It provides operational and price advantages based on traditional and integrated architecture. VMware vSan, Nutanix, Hpe Simlivity, Fujitsu Primeflex for vSAN are examples of this architecture.
You can read my VMware vSan article here.

Yorum yapılmamış
You can leave the first : )